A Comprehensive Guide to Microservices Architecture: Transitioning from Monolith, Patterns, and Pitfalls to Avoid
Estimated reading time: 18 minutes
Key Takeaways
- **Microservices architecture** enables modular, scalable, and resilient systems by decomposing applications into small, independent services.
- The shift from monolith to microservices supports faster deployments, greater team autonomy, and targeted scaling.
- Applying well-known microservices patterns like API Gateway, Database per Service, Circuit Breaker, Event Sourcing, and CQRS is key for success.
- Beware of common pitfalls such as over-fragmentation, complex communication, data consistency issues, and operational overhead.
- Adhering to industry best practices like automating deployment, enforcing observability, and designing clear service boundaries maximizes benefits.
Table of contents
Understanding Microservices Architecture
Core Principles of Microservices Architecture
Microservices architecture is grounded on a few fundamental principles that distinguish it from monolithic designs:
- Independent Deployability
Each microservice can be developed, deployed, and scaled on its own lifecycle, without requiring a full application redeployment. This independence accelerates innovation and reduces downtime. (AWS Microservices, Microsoft Learn) - Decentralized Data Management
Instead of sharing a centralized database, each service owns and manages its own data store. This separation prevents tight coupling at the data layer and eases schema changes or technology swaps within each service. (Microsoft Learn, Sanity.io Glossary) - Scalability and Resilience
Services can scale independently, improving resource utilization. Faults in one microservice remain contained, preventing cascading failures across the entire application. This fault isolation enhances overall system resilience. (Softjourn Insights, AWS Microservices)
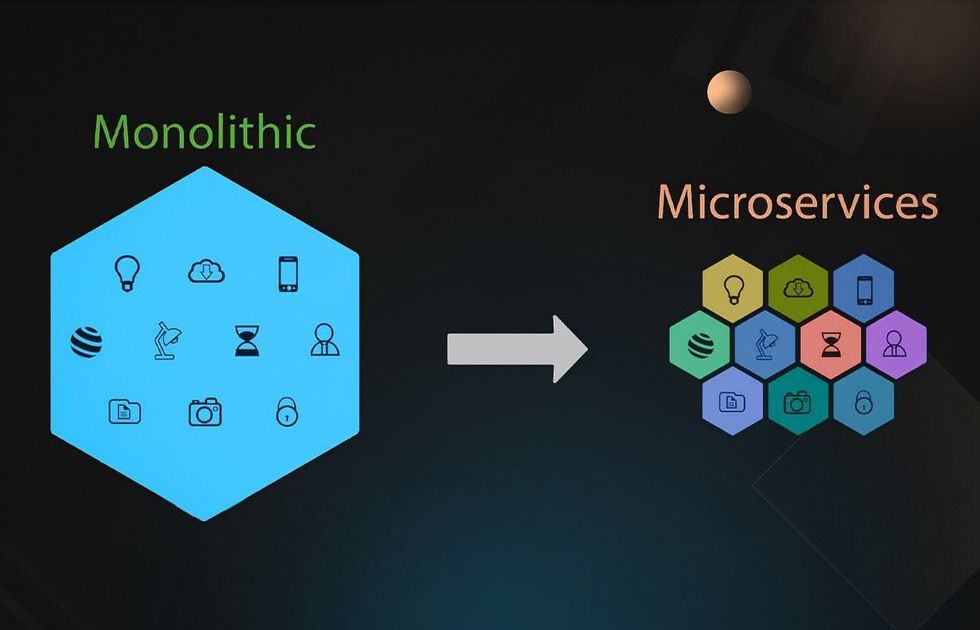
Microservices Architecture vs. Monolithic Architecture
- Monolithic Architecture packages all UI, business logic, and data access layers into a single deployable unit and typically uses a shared database. Changes require redeploying the whole application. (Sanity.io Glossary)
- Microservices Architecture decomposes functionality into multiple autonomous services aligned with specific business domains. Each service runs independently, owning its own data and communicating over network protocols. (Softjourn Insights)
| Aspect | Monolithic Architecture | Microservices Architecture |
|---|---|---|
| Deployment | Single, large deployable unit | Multiple independently deployable services |
| Data Management | Shared database | Database per service, decentralized persistence |
| Scalability | Scale entire app | Scale hot spots independently |
| Technology Stack | Usually uniform | Polyglot – different technologies per service possible |
| Change Impact | Risky system-wide change | Localized changes, faster deployments |
This shift from monolith to microservices unlocks agility, better team autonomy, and efficient scaling. (AWS Microservices, Microsoft Learn, TechCircleNow)
Transitioning from Monolith to Microservices
Why Move from Monolith to Microservices?
Organizations are increasingly adopting microservices to overcome the limitations of monolithic applications. Key drivers include:
- Scalability Improvements
Microservices let you scale only the parts of the system that experience high load, instead of scaling the entire monolith. This targeted scalability saves resources and streamlines operations. - Faster and Safer Deployments
Independently deployable services enable continuous integration and delivery. Updates to one service don’t require full system redeployment, reducing downtime and risk. - Greater Team Autonomy
Smaller, focused services allow development teams to own specific domains and parallelize work without interfering with other teams’ codebases. - Improved System Resilience
Isolation of failures to single microservices prevents entire system outages caused by bugs or crashes in one component.
(AWS Microservices, Softjourn Insights)
Step-by-Step Migration Strategy
- Assess Readiness and Identify Domain Boundaries
Use Domain-Driven Design (DDD) to analyze your monolithic application. Identify natural boundaries where functionality aligns with business domains. Target high-value or frequently changing areas for initial service extraction. - Apply the Strangler Fig Pattern
This incremental approach routes parts of the monolith’s functionality to new microservices, progressively replacing existing components and shrinking the monolith. - Extract Cohesive Services
Break out tightly coupled modules into standalone microservices. Each should expose well-defined APIs and maintain its own data store, avoiding shared databases between services for loose coupling. - Build Foundational Platform Capabilities
Establish CI/CD pipelines, containerization (e.g., Docker), service discovery mechanisms, and centralized logging/monitoring early. These enable smoother management as the system grows distributed. (TechCircleNow) - Iterate and Improve
Start small and gather feedback on observability, deployment practices, and service interactions. Gradually expand the migration, refining architecture and operational processes.
Challenges and Considerations
- Distributed System Complexity
Network calls introduce latency, partial failures, and potential cascading issues. Design for resilience through retries, fallbacks, and circuit breakers. Observability is critical to diagnose issues in this environment. (Microsoft Learn) - Shifting Consistency Models
Moving from a single shared database to distributed data stores means giving up strong consistency for eventual consistency models, complicating transaction management across microservices. - Increased Operational Overhead
Managing many independent services requires sophisticated DevOps tooling and automation to maintain reliability and deployment speed. - Cultural Transformation
Teams must embrace new roles and responsibilities such as “you build it, you run it,” owning service reliability and participating in continuous delivery workflows.
Common Microservices Patterns
Implementing a microservices architecture effectively involves applying well-established microservices patterns that solve common architectural challenges:
API Gateway
- Purpose: Acts as a single entry point to multiple microservices. It handles request routing, authentication, rate limiting, and response aggregation.
- Benefits:
- Decouples clients from backend service complexity.
- Simplifies cross-cutting concerns like security and caching.
Database per Service
- Purpose: Each microservice maintains its own dedicated database or schema.
- Benefits:
- Prevents tight coupling at the data level through isolation.
- Allows independent schema evolution and better data ownership.
- Supports polyglot persistence strategies.
Circuit Breaker
- Purpose: Prevents cascading failures by wrapping calls to dependent services and “opening” the circuit when failures exceed a threshold.
- Benefits:
- Improves system resilience by detecting failing services early.
- Allows fallback behaviors or retries, maintaining service availability during partial outages.
Event Sourcing
- Purpose: Stores all changes to application state as a sequence of immutable events instead of just current state snapshots.
- Benefits:
- Provides detailed audit trails.
- Enables temporal queries and reconstruction of past states.
- Facilitates asynchronous communication and eventual consistency.
CQRS (Command Query Responsibility Segregation)
- Purpose: Separates the write model (commands) from the read model (queries), often using different data stores optimized for each interaction type.
- Benefits:
- Enhances performance under high-read or high-write loads.
- Simplifies complex domain models, especially when paired with event sourcing.
These patterns directly address challenges in coupling, resilience, data management, and scalability within microservices architectures.
Common Microservices Pitfalls to Avoid
While microservices offer many advantages, several pitfalls can undermine their benefits if not properly addressed:
Over-fragmentation
- Problem: Excessive splitting into very small, narrowly focused services leads to complex inter-service communication, difficult deployments, and high operational overhead.
- Mitigation: Start with coarse-grained services aligned to meaningful business capabilities. Only split further when clear benefits outweigh complexity.
Complex Communication and Tight Coupling
- Problem: Heavy synchronous HTTP calls between services create latency and risk cascading failures, eroding system resilience.
- Mitigation: Design clean, versioned APIs. Favor asynchronous communication such as messaging and event-driven architectures where possible to decouple dependencies.
Data Consistency Challenges
- Problem: Distributed transactions are difficult to manage, risking stale or inconsistent data across services.
- Mitigation: Implement eventual consistency through patterns like sagas. Ensure each service maintains its own data integrity constraints and ownership.
Monitoring and Observability Difficulties
- Problem: Without centralized logging and distributed tracing, debugging failures in a distributed system is extremely challenging.
- Mitigation: Invest early in observability infrastructure, including aggregated logging, metrics collection, distributed tracing, and health checks.
Underpowered Platform and Tooling
- Problem: Lack of automation for deployment, testing, and monitoring leads to errors, slow release cycles, and fragile operations.
- Mitigation: Build robust CI/CD pipelines, use container orchestration tools, and automate infrastructure provisioning and testing.
Best Practices for Implementing Microservices Architecture
Drawing on the lessons from patterns and pitfalls, here are essential best practices:
- Align Services with Business Capabilities
Define clear service boundaries around domains and subdomains to ensure strong cohesion and loose coupling. - One Data Store per Service
Avoid shared databases. Each service should control its own persistence layer to enable independent evolution. (Microsoft Learn) - Favor Asynchronous Communication
Asynchronous messaging reduces latency and dependencies, increasing resilience and scalability. - Implement Comprehensive Observability
Logging, metrics, tracing, and health monitoring must be integral to every service for rapid diagnostics and uptime. - Automate Everything
Continuous integration, delivery pipelines, automated testing, and rolling deployments ensure fast, reliable releases. (TechCircleNow) - Define and Version APIs Clearly
Maintain backward compatibility and manage service upgrades without disrupting consumers. - Choose Service Size Judiciously
Services should be manageable by a single team and large enough to reduce excessive network overhead. - Plan for Failure
Use circuit breakers, timeouts, retries with exponential backoff, and graceful degradation to build robust fault tolerance.
Adhering to these principles maximizes the benefits of microservices architecture in scalability, maintainability, and observability. (Softjourn Insights, AWS Microservices)
Conclusion
Adopting a microservices architecture brings significant benefits:
- Improved scalability by targeting resource use to high-load services
- Better fault isolation limits impact of failures
- Faster feature delivery through autonomous teams and independent deployability
- Enhanced team autonomy driving innovation
However, this architectural style also introduces challenges like distributed system complexity, eventual consistency models, operational overhead, and necessary cultural changes.
A successful transition from monolith to microservices depends on:
- Careful assessment and incremental migration strategies
- Wise application of proven microservices patterns such as API Gateway, Database per Service, Circuit Breaker, Event Sourcing, and CQRS
- Avoidance of identified microservices pitfalls using best practices in design, platform, and culture
For further learning, explore:
- Comprehensive guides by cloud providers such as AWS and Microsoft Azure
- Domain-Driven Design literature for effective service boundary identification
- Distributed systems patterns covering sagas, observability, and event-driven architecture
A well-planned, pattern-informed microservices adoption ensures a more agile, scalable, and maintainable software ecosystem.
By embracing microservices architecture with clarity and discipline, organizations can harness the full power of modern software engineering to meet evolving business demands.
DevOps Best Practices
Cloud Computing Trends
Digital Transformation Strategy Guide
Future of Work Trends 2025
Tech Industry Research Insights
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is microservices architecture?
- Microservices architecture is a software design style where an application is composed of small, autonomous services that communicate over lightweight protocols, allowing independent development, deployment, and scaling.
- How does the transition from monolith to microservices work?
- The transition involves assessing your current application, identifying domain boundaries using Domain-Driven Design, incrementally extracting services via patterns like the Strangler Fig, building platform capabilities, and iterating improvements. (TechCircleNow)
- What are common patterns used in microservices?
- Common patterns include API Gateway, Database per Service, Circuit Breaker, Event Sourcing, and CQRS, each addressing challenges like service communication, data ownership, resilience, and scalability. (Microsoft Learn)
- What are pitfalls to avoid when adopting microservices?
- Avoid over-fragmentation, complex synchronous communication, data consistency issues, inadequate observability, and underpowered tooling to prevent operational difficulties and degraded system resiliency.
- What are best practices for microservices adoption?
- Align services to business capabilities, use one data store per service, favor asynchronous communication, implement comprehensive observability, automate delivery pipelines, clearly define APIs, and design for failure to ensure success.

